Understanding Key Geographical Features of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece
The world as we know it today is a product of billions of years of weather erosion, climate changes and continental drifts. Even the activities of humans have changed the geography of most areas of the world. The landscape of the modern world is practically a distorted image of its original appearance.
But that does not make ancient geography less fascinating. Let us take ancient Greece, for example.The geography of ancient Greece can be considered primitive in our modern eyes, but back in those days, the Greek landscape was an advanced landscape compared to other lands. It was also littered with an abundance of natural resources, which the ancient Greeks made use of in astonishing ways.
The Peninsula
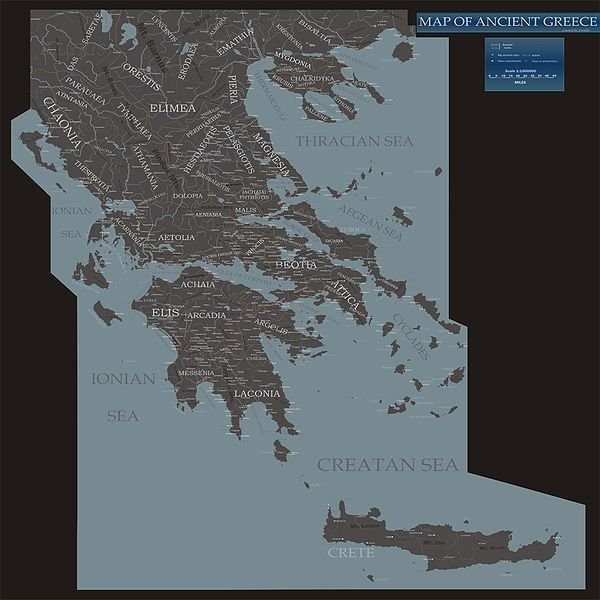
Greece is surrounded by water on three sides, making it a peninsula. It has several smaller peninsulas protruding from its shores, making the country fertile ground for ports and harbors. Islands surround the main land, giving ancient Greece a multitude of varying cultures and types of people. This, plus the fact that most of the main land is composed of mountains, inspired the Greeks to travel mostly by water using boats. Ancient Greeks became great sailors because of this, which is also the reason why they had the might, the drive and the ability to cross into other lands by sea and conquer them.
The Main Land
As the natural harbors of the smaller peninsulas of Greece inspired thriving markets of seafood and adventures into the high seas, the main land bustled with cities built around mountains. The soil around the mountains were very fertile, ideal for farms to pop up in all corners of the ancient Greek world. Vegetables and fruits were in abundance, inspiring trade between cities through roads that were built to complement the rocky mountain paths. There were not a lot of roads back then, but there were enough to establish civilized trade routes and faster travel between cities.
The mountain ranges of Greece were epic in scope, inspiring legends and heroic stories, which is probably why a lot of the elements of Greek mythology were so legendary. The highest point in Greece is Mount Olympus, the “home of the gods”, at a height of 2,919 meters above sea level. A lot of mountain ranges are spread across Greece with some plain sprinkled in. These mountains, like the islands of Greece, promoted regionalism, further diversifying the culture and the philosophy of ancient Greeks.
Famous Locations
With a geography that proved bountiful life for ancient Greeks, they managed to establish cities and towns that became busy with activities that involved art, music and literature. The famous places in ancient Greece include Sparta, a small town that was always protected by its mightiest fighters from foreign invaders, Olympia, the birth place of the Olympic games, and Athens, the center of democracy and art in the then civilized world. Athens is considered by many as the cradle of Western civilization thanks to its wonderful architecture and a society built on the appreciation for the arts. The geography of ancient Greece allowed ancient Greeks to build a society that would last forever in the hearst and minds of people from all over the world.
References
https://www.crystalinks.com/greekgeography.html
https://greece.mrdonn.org/geography.html
https://www.ancientgreece.com/s/Geography/
Photo Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; GNU Free Documentation License / by Astaldo