The Male and Female Reproductive Parts of A Flower
How Do Plants Reproduce?
The reproductive parts of a flower are actually the most important parts of a flower. This is because a flower’s main function is to reproduce so that the plant can pass on its genes. A flower usually reproduces by creating seeds that are then dispersed and eventually become new plants.
Female Reproductive Parts of A Flower
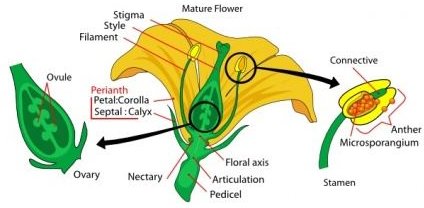
[caption id=“attachment_130709” align=“aligncenter” width=“755”] The various parts of a flower[/caption] The main female reproductive parts of a flower are the carpels, which are fused together in most flowers to form a pistil. The pistil is usually found in the center of the flower, and is essentially a home for the ovules, or eggs. A pistil has three parts: a sticky part at the top called a stigma, the thin tube leading downward called a style, and the sac at the bottom called an ovary. When the pollen, which is the male gamete (corresponding to sperm in animals), reaches the pistil, it often becomes stuck to the stigma. The pollen then travels down the style into the ovary, where it meets with the ovules and fertilizes them.
The various parts of a flower[/caption] The main female reproductive parts of a flower are the carpels, which are fused together in most flowers to form a pistil. The pistil is usually found in the center of the flower, and is essentially a home for the ovules, or eggs. A pistil has three parts: a sticky part at the top called a stigma, the thin tube leading downward called a style, and the sac at the bottom called an ovary. When the pollen, which is the male gamete (corresponding to sperm in animals), reaches the pistil, it often becomes stuck to the stigma. The pollen then travels down the style into the ovary, where it meets with the ovules and fertilizes them.
Male Reproductive Parts
The male reproductive parts of a flower are much simpler than the female ones. Called stamens, these reproductive organs are made up of two parts: anthers and filaments. The anther is the part of the organ that produces pollen, and the filaments hold up the anthers. There are often several stamens for every one pistil. This is because having multiple stamens increases the number of pollen grains available, which make it more likely than one of the pollen grains will become stuck to the stigma, travel down the style into the ovary, and fertilize the ovules to produce seeds.
How do They Meet?
In order for the ovules in the ovary to be fertilized, the pollen needs to get inside the ovary. How does this happen? Actually pollination can occur in many different ways. Sometimes, the wind blows the pollen towards the pistil so that it gets stuck on the stigma. Other times, an animal brushes by the stamens and carries the pollen on its fur until it falls off near a pistil, or an insect lands on an anther and then lands on the top of a pistil. Remember that not all plants are self-fertilizing, which means that some plants become fertilized by the pollen from other plants, so pollen may travel a long distance before it actually meets up with an ovule to fertilize. In summary, there are two main reproductive parts of a flower, a male part and a female part. The stamen, which is male, produces pollen; the pistil, which is female, houses the ovule. When the two meet, they produce a seed, which creates a new generation of plants.
References
The Great Plant Escape. “Plant Parts - Flowers.” Biology Corner. “Flower Structure and Reproduction.”