Technological Changes in Education: How Teachers Can Adapt
Technological Changes in Education
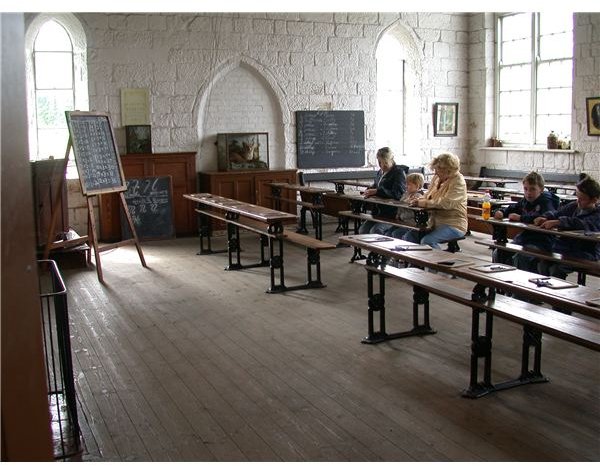
Education has evolved with the times, particularly from the last few decades in the 20th century, into the 21st century. Gone are the one room schoolhouses, with their rows of wooden chairs, benches, and desks - other than as tourist attractions and reminders of simpler times.
Today’s classroom is more likely to be a computer lab, a room with rows of students using laptops, or perhaps students listening to a podcast or taking in a video lecture.
Technological changes in the educational industry have created new ways to teach and to learn.
Teachers have had to adopt new instructional methodologies, while students usually eagerly embrace this “new” style of learning. Technological changes allow teachers to access information on a global scale via the Internet, to enhance their lessons. Likewise, students can use the vast resources of the Internet to enrich their learning experience.

Even earlier technology, such as slide projectors and overheads with transparencies, have given way to PowerPoint presentations or streaming videos projected for viewing by entire classes or entire school bodies in auditoriums. From audio and video technology, to podcasts and interactive tutorials, to e-learning and real-time online lectures, educational technology is here to stay.
Overview of Educational Technology
Educational technology simply refers to using various forms of technology to support and enhance the learning process. It also goes by other terms, including instructional technology and e-learning, although they are not totally synonymous. A more accurate definition for educational technology is “technology as it impacts upon the learning process … in delivering learning materials, facilitating communication and providing assessment and feedback.” [1]
Educational reform efforts during the 1980s and 1990s played a significant role in the initiation and implementation of educational technology. Many school systems, during school restructuring initiatives, incorporated the technological changes in the educational industry as focal points. Their efforts back then, opened the door for even greater advances of educational technology as the 20th century ended. Computers, educational software, assistive technology, virtual classrooms, and other technological changes in education became more commonplace as the 21st century began.[2][3]
Popular Forms of Educational Technology
The following list offers a look at some of the most popular forms of educational technology, gaining acceptance at a rapid pace.
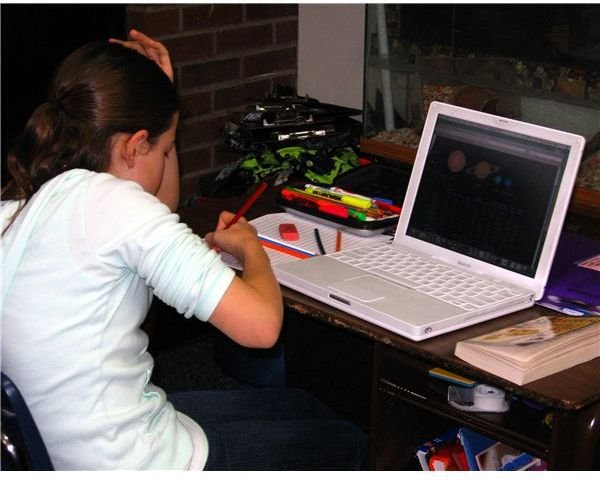

Computers and Laptops
Most classrooms these days, from grades K-12 through colleges, typically have at least one resident computer or laptop. Initiatives on local, state, and national levels sometimes sponsor and fund drives to equip classrooms with enough computers or laptops for each student. As laptops become less expensive and more compact, they are increasingly popular alternatives to bulkier, stationary desktop computers.
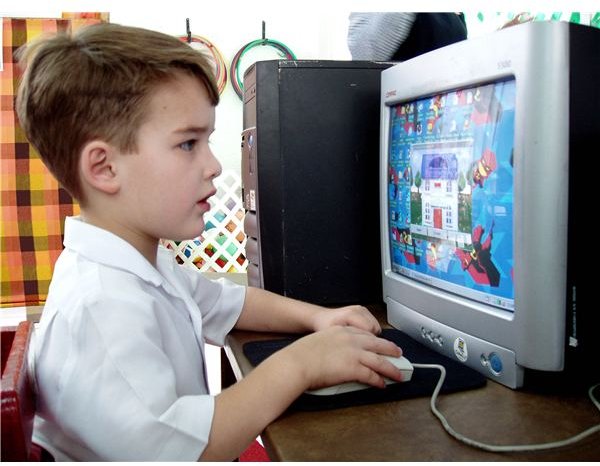

Educational Software
The proliferation of computers and laptops in classrooms has created a substantial market for educational software. From simple kindergarten level games to aid students in learning their alphabet and numbers, to senior high level courses in calculus and biology, educational software adds a fun element to learning, while also promoting significant learning skills. In addition to initial instruction, most software programs include reinforcing learning elements, as well as assessments, to further ensure students improve their comprehension and implementation of a subject’s concepts.
Audio, Video, and Other Multimedia Presentations

Podcasts, streaming videos, PowerPoint, and other forms of multimedia presentations provide an enriched learning experience for students. For instance, teachers can record lectures in podcasts, as well as share other important news and information with students.[4]
YouTube has also become a widely used teaching and learning tool. Instructors can post their own instructional videos, while students can likewise create videos depicting projects or other learning experiences.[5]
Social Media

There seems to be no end to the uses of social media online. From keeping in touch with friends and family, or promoting a business, on Facebook, to tweeting about activities on Twitter, to setting up social networks on Ning to share resources and tips with like-minded people, to promoting one’s academic or business endeavors with a professional profile on LinkedIn - “techno savvy” teachers can incorporate any or all of these forms of technology into the curriculum, depending on students’ ages. Students can learn the various technology platforms, of course, but they can also develop social and communication skills, and older students can develop business and professional skills. (See the image of the header from this writer’s Ning group - click for larger view).
E-Learning
E-learning is the ultimate form of educational technology, at least in this writer’s opinion, as a doctoral student in an Ed.D. program with a dual concentration in - what else - Educational Technology and E-Learning! Online learning provides one of the most flexible and convenient means to pursue higher education, especially for busy adult learners. Laptops and 24/7 internet access to course materials and virtual classrooms add even greater measures of freedom and manageability to e-learning.
Following is a screenshot from the opening assignment in a new course entitled Instructional Design and Engaging E-Learning Activities, ironically enough (click on the image for a larger view). This offers merely one perspective on what a virtual classroom looks like. This screenshot depicts the assignment for participation in a discussion question in this particular course. Students and the instructor then have the opportunity to respond or comment on other entries.
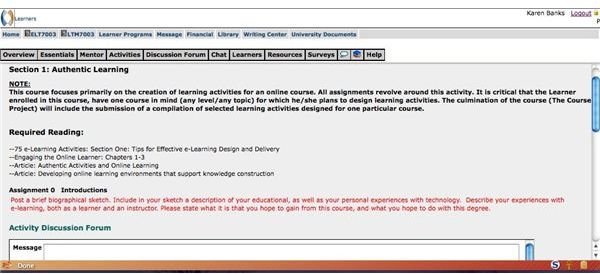
Technological changes in the education industry have created greater opportunities for teachers and students alike. Teachers incorporate new instructional methodologies as they draw from global resources via the Internet. Students enjoy enhanced learning environments that often include online research, computer-based lessons, or virtual classroom interaction. Other technological changes in education, including online evaluations and assessments, provide new tools for teachers and challenging learning experiences for students. Educational technology has transformed the old one room schoolhouse model into a virtual classroom with a global student body.
References
[1] Educational Technology Insight. Why Educational Technology?
[2] Online Education: Learning and Teaching in Cyberspace, by Greg Kearsley. (2000). Research About Online Education. California: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning.
[3] Exploring Technology and School Reform, by Andy Carvin. Education Reform History.
[4] Poducate Me. Podcasting in Education.
[5] Converge. Is Education Ready for YouTube? by Sara Cardine.
Resources
Facebook: Teacher’s Guide to Using Facebook.
LinkedIn: LinkedIn New User Starter Guide.
Ning: Create a Social Networking Site.
Twitter: Using Twitter in Education. From KQED Education
Image Permissions
All images (excluding screenshots) from morgueFile Free Photos with the following permission: You are allowed to copy, distribute, transmit the work and to adapt the work. Attribution is not required.
Virtual classroom course screenshot and Ning network header screenshot provided by this article’s author, K’Lee Banks.
